Gravity Forms is one of the most powerful form builders available for WordPress — but it has one limitation:
It does not offer a built-in Rich Text Editor (WYSIWYG) field.
For websites that rely on user-generated content—such as blogs, directories, reviews, job listings, or frontend post submissions—a basic textarea simply isn’t enough.
A proper Rich Text Editor allows users to format text with:
- Headings (H1–H6)
- Links & Media
- Bold, Italic, Underline
- Bullet and Numbered Lists
- Images
- Blockquotes
- Inline styles like alignment, colors, and spacing
So in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to add a fully functional Rich Text Editor field inside Gravity Forms using custom code — without installing an extra plugin.
What This Solution Supports
- Works on frontend
- Uses TinyMCE (WordPress default editor)
- Supports media uploads
- Outputs clean formatted HTML
- Works with Gravity Forms Post Creation Add-On
- Prevents raw HTML from showing in visual mode
Why You Need a Custom Rich Text Editor in Gravity Forms
A normal textarea field cannot store or render formatted content like:
- Titles and headings
- Styled paragraphs
- Embedded media or images
- Links and structured lists
If you’re building forms like:
- Blog submission form
- Directory or listing submission
- User reviews
- Job listing submission
- Knowledgebase article submission
- Community-generated content
…then users need a proper editor — not a plain text field.
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1 — Add This Code to Your functions.php
Copy and paste the following entire code block into your theme’s functions.php or a custom plugin:
( Code already formatted, so no changes needed — paste exactly as provided.)
Download code here: Gravity form Rich text-editor code
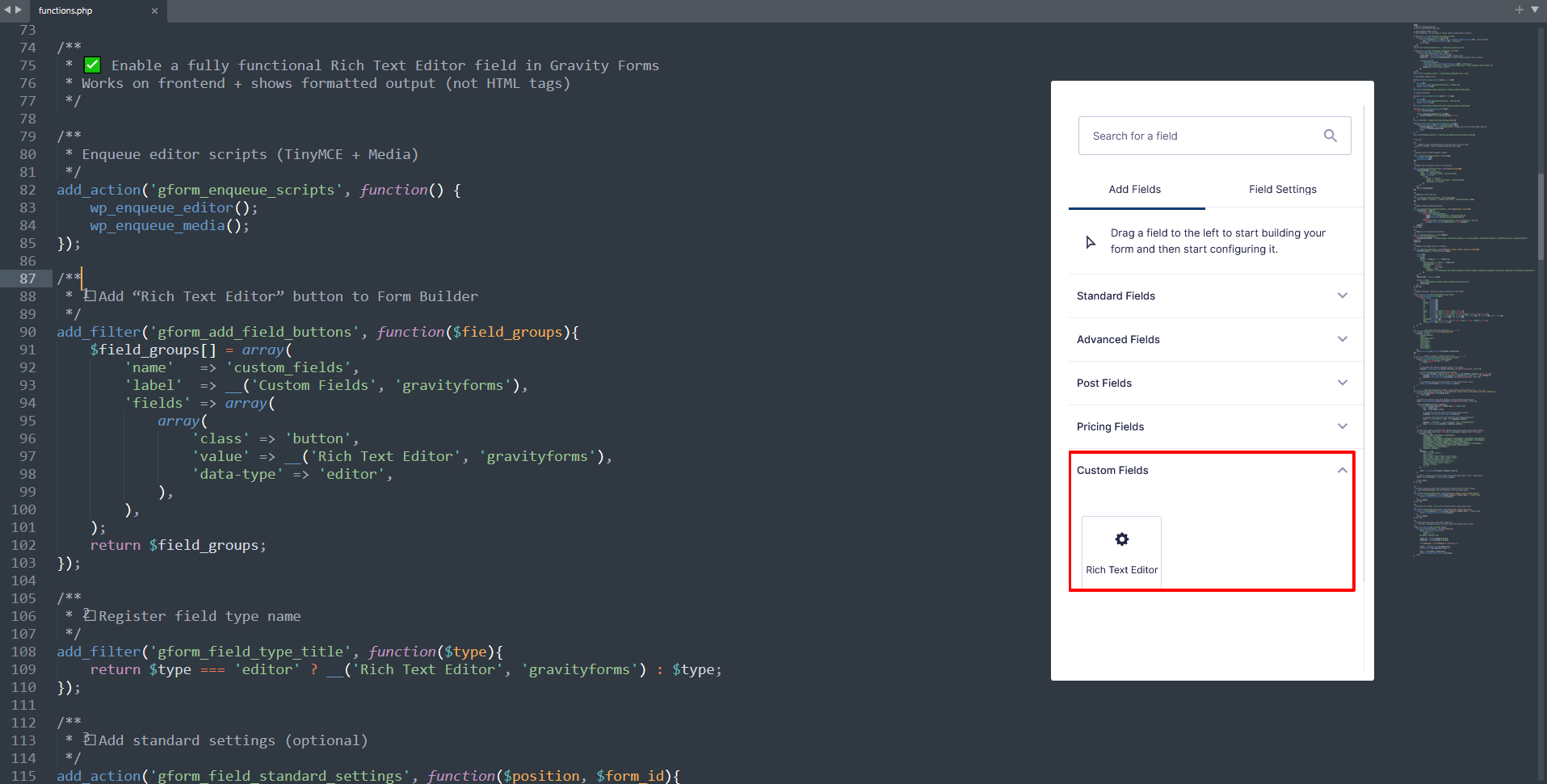
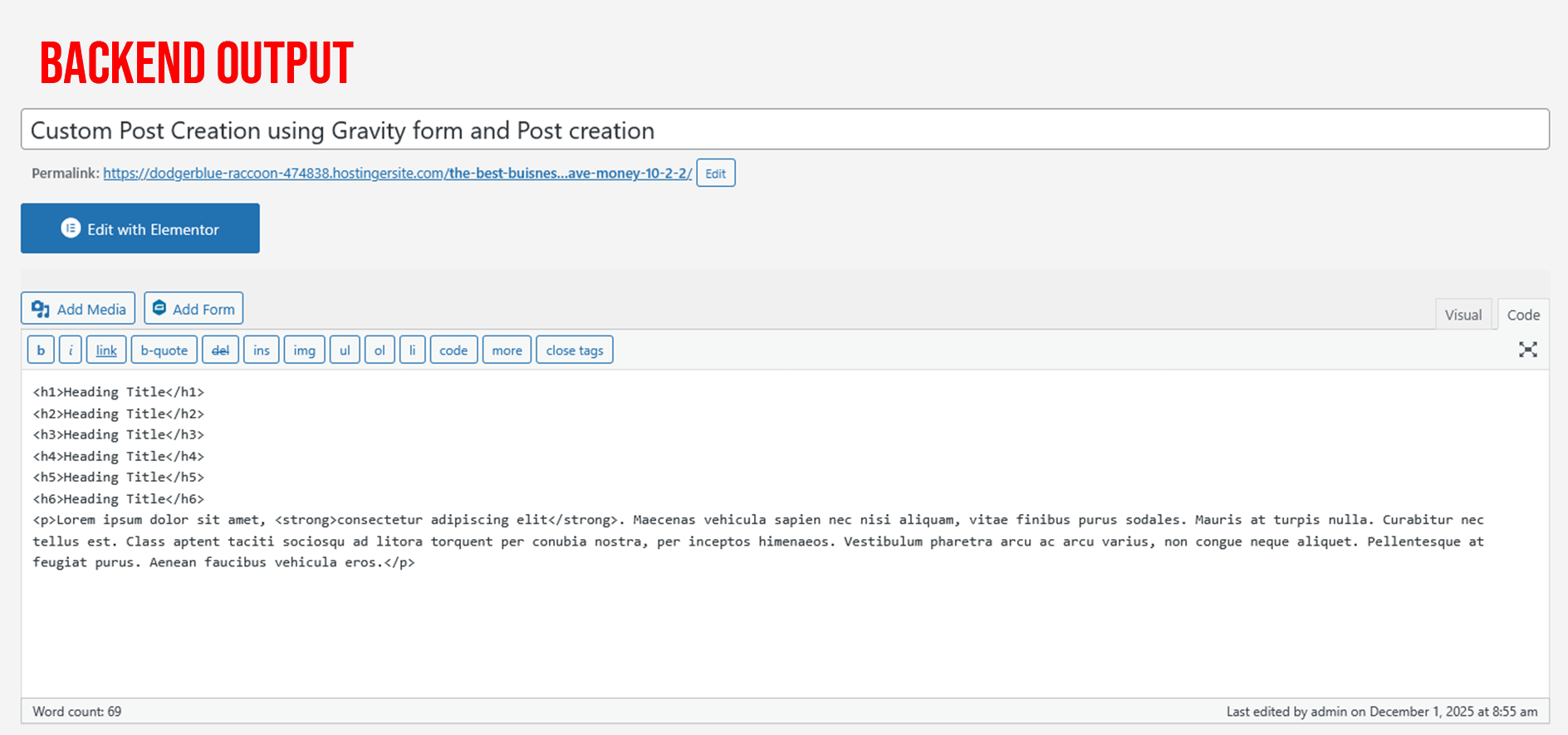
Once added, Gravity Forms will display a new field called: Rich Text Editor under the “Custom Fields” tab.
Step 2 — Create a New Gravity Form
- Go to Forms → New Form
- Give it a name (Example: Blog Submission Form)
- Add standard fields like:
- Name
- Post Title
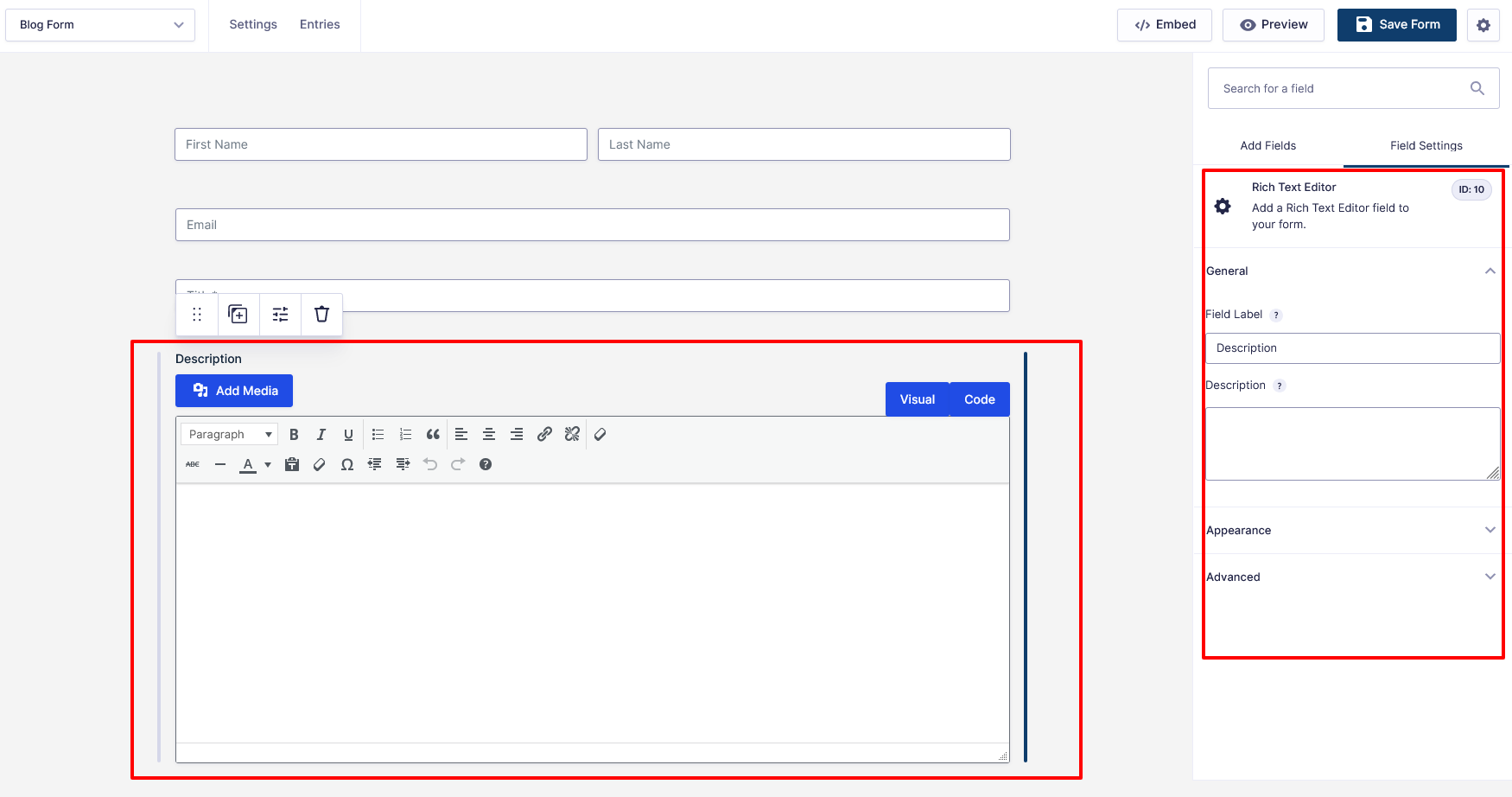
- Add your new field: Rich Text Editor
- Save the form
Tip: Note the Field ID for later (Example: Field ID: 10).
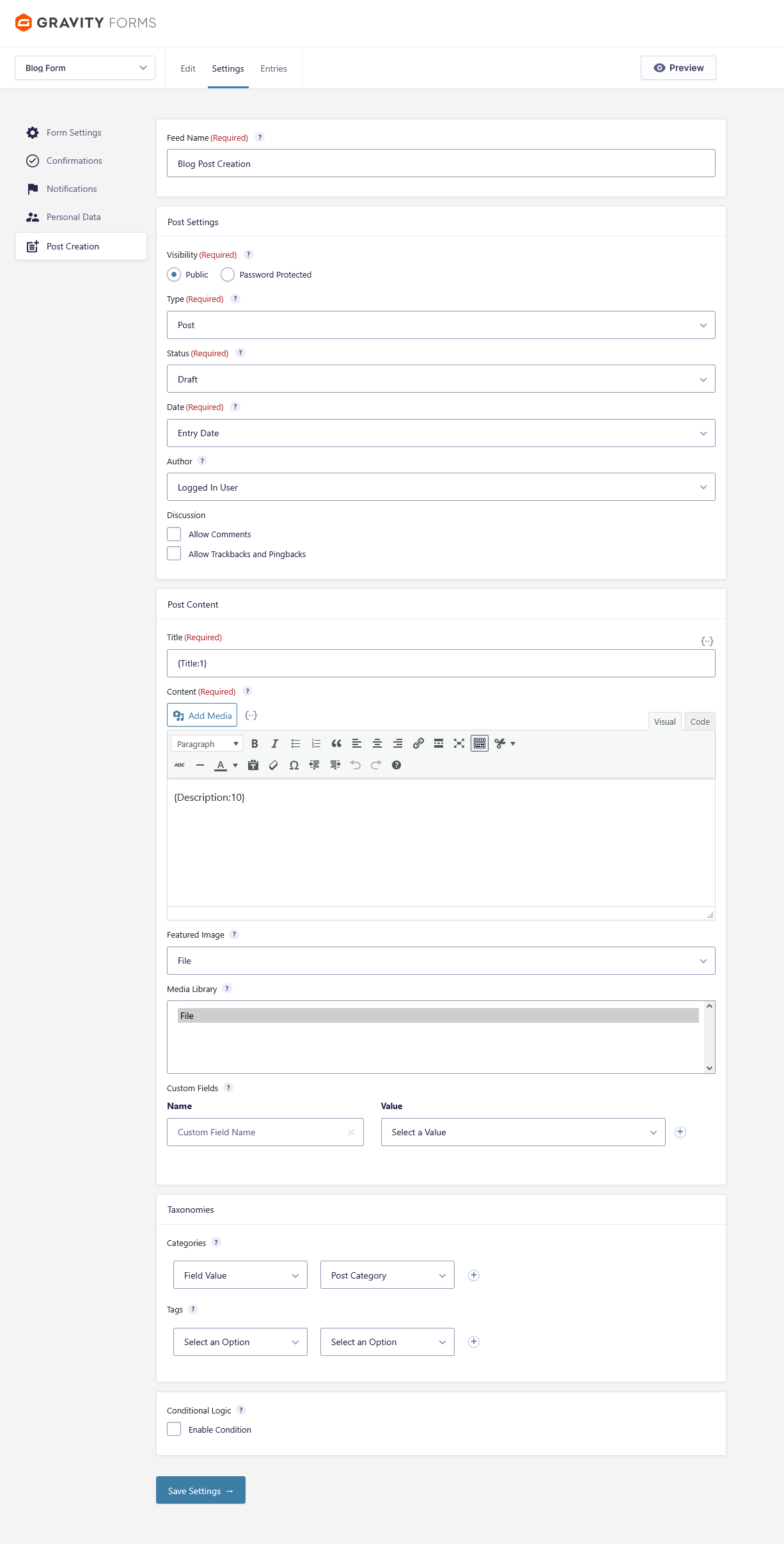
Step 3 — Configure Gravity Forms Post Creation Add-On
- Go to Form → Settings → Post Creation
- Create a new feed
- Settings example:
| Setting | Example |
| Post Type | Post (or Custom Post Type) |
| Status | Draft (recommended for testing) |
| Author | Logged-in User |
| Title | {Post Title:1} |
| Content | {Description:10} ← must match Rich Editor Field ID |
(Optional) Map:
- Categories
- Tags
- Featured Image
- Custom fields
Important: Ensure the content field uses the field ID of the Rich Text Editor.
Step 4 — Add the Form to a Page
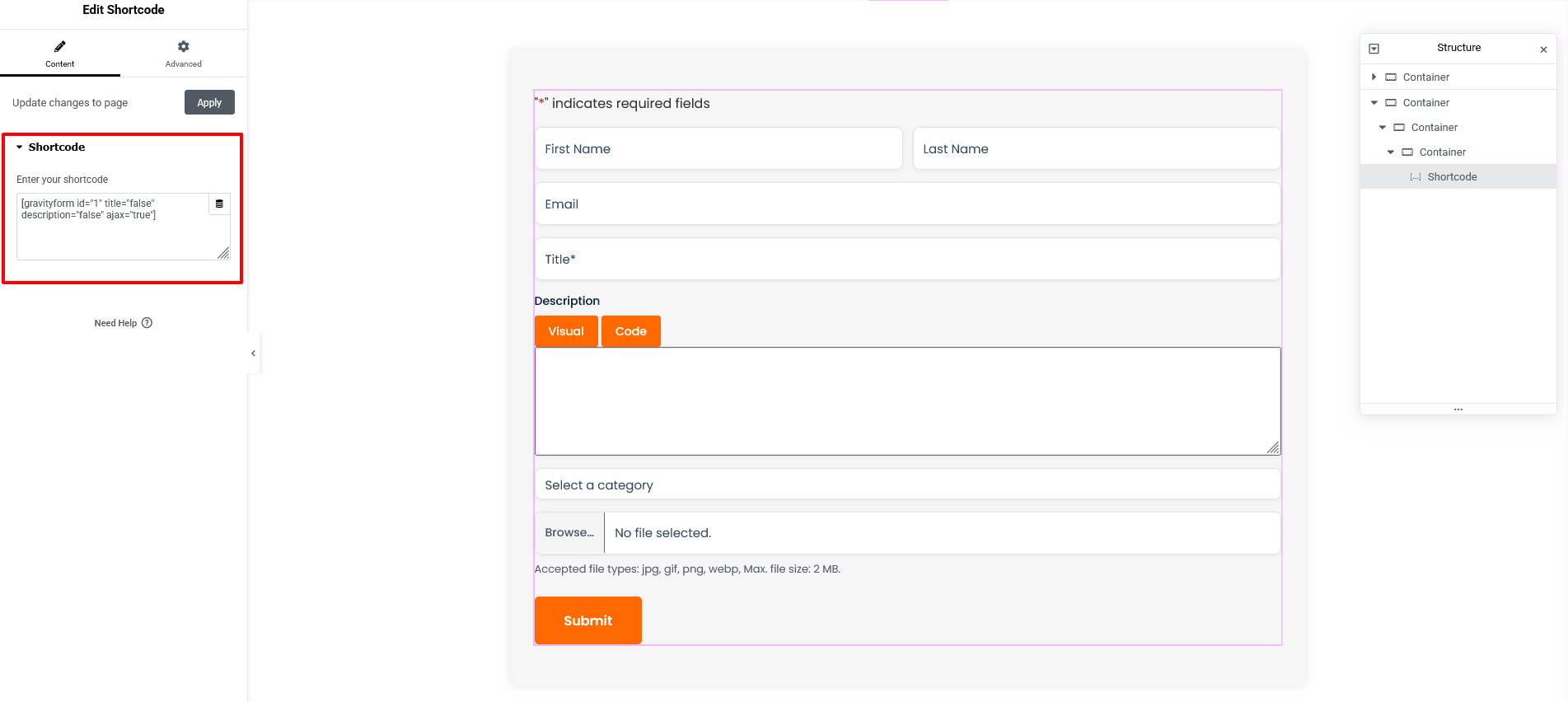
Use this shortcode anywhere:
[gravityform id="123" title="true" description="false" ajax="true"]
Replace 123 with your form ID.
Publish your page (example: Submit a Blog).
Step 5 — Test the Submission
- Open the form on the frontend
- Format content using the editor (bold, headings, images, lists, etc.)
- Submit the form
- Check:
Posts → All Posts
You should see a new post created — with formatting preserved.
- In WP Admin go to Posts → All Posts and find the new post (status based on your feed setting).
- Click Edit on the post and check the Visual tab in the editor — the content should render as formatted HTML (not raw HTML tags).
- View the post on the frontend and confirm headings, lists, images and styling display correctly.
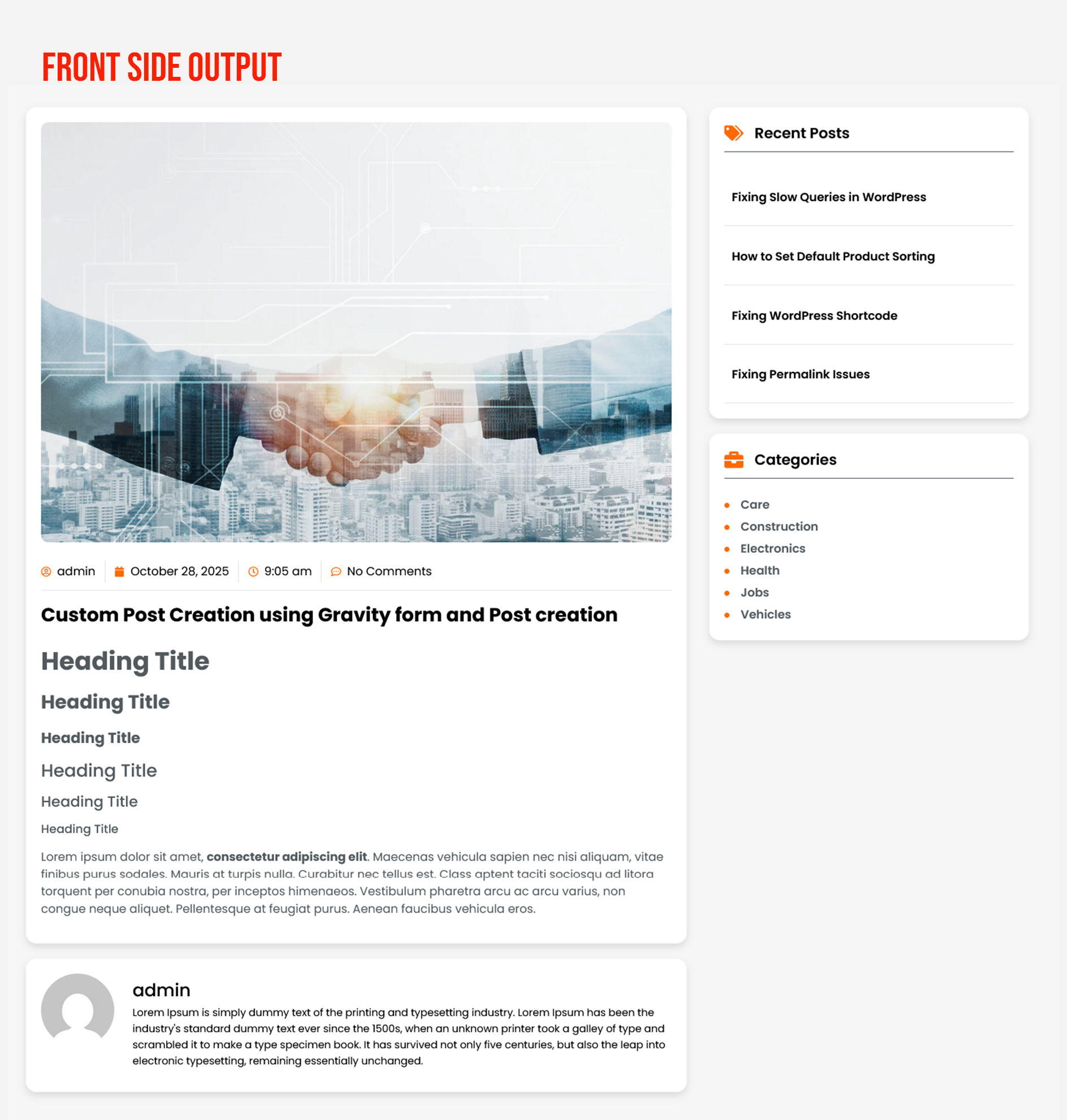
Final Result
You now have a fully working frontend content editor inside Gravity Forms — without additional plugins.
- Works with WordPress media uploader
- Supports formatting, links, images, headings
- Perfect for guest posting, user-generated content, and custom submission workflows
Conclusion
Adding a rich text editor to Gravity Forms dramatically improves the user experience for forms involving long-form content.
Whether you’re building a submission portal, directory, review system, or frontend publishing workflow — this upgrade makes Gravity Forms behave more like a real blogging platform.